Understanding how to calculate profit margins is a core responsibility of accountants and many other finance professionals. Profit margins are an easy way to determine if a company is profitable (making more money than it spends) and can inform decisions like investing options and budgeting.
What Is a Profit Margin?
A profit margin is a straightforward measure of profitability: It looks at how much a company makes per $1 of revenue generated. Or, to put it another way, a profit margin shows how much revenue a company can keep as profit. Profit margins are typically expressed as percentages. For example, a 60% profit margin would mean a company has a profit of $0.60 for every dollar of revenue generated.
Profit margins can be negative or positive, and companies with negative profit margins can still survive. Ultimately, companies want to maximize profits, which they can do by either cutting expenses or by increasing revenue.
Who Needs to Calculate Profit Margins?
Calculating profit margins is a core responsibility in many accounting roles and careers in finance. For instance, investment bankers use profit margins to determine if a company is profitable and worth the investment. Financial analysts rely on profit margins to help businesses make informed decisions. Understanding how to calculate profit margins can also help certain accountants, like certified management accountants, build budgets because they can see what areas are causing the most loss in profits.
Profit margins are ultimately useful for investors of any kind — profitable companies may be a less risky investment, and knowing a company’s profit margins can inform investing decisions.

Bank of America Investment Banking
Apply analysis and communication skills to advise clients and help them make informed investing decisions with this free job simulation from Bank of America.
Avg. Time: 4 to 5 hours
Skills you’ll build: SWOT analysis, financial analysis, M&A screening, cross-team collaboration, ECM/DCM, financial modeling, DCF, valuation, communication, presentation
Profit Margin Formulas
You can calculate different types of profit margins, including net profit, gross profit, and operating profit.
- Gross profit looks at earnings after the cost of goods sold (COGS).
- Net profit looks at profits after everything else has also been taken out, like taxes, marketing expenses, rent, and debts.
- Operating profit is how much money the company has left over after covering operating expenses (like COGS and employee wages), but before paying taxes and interest.
How to Calculate Gross Profit Margin
Gross profit is revenue (or net sales) minus the direct cost of goods or services. For example, if a company sells t-shirts, its gross profit would be how much it made from selling the shirts minus how much the company paid for the shirts. The margin is the gross profit divided by the total revenue, which creates a ratio. You can then multiply by 100 to make a percentage.
The formula for calculating gross profit margins is:
Gross Profit Margin = ( (Net Sales – COGS) / Revenue ) x 100
In this formula:
- Net sales can be used interchangeably with revenue for the sake of this formula — it is simply how much money was generated from selling products, goods, or services.
- COGS is the cost of goods sold (raw materials, labor, manufacturing expenses).
- Net sales minus COGS gives you gross profits.
- Multiply by 100 at the end of the formula to create a percentage.
How to Calculate Net Profit Margin
Net profit or net income is how much the company makes after removing all expenses. These expenses include taxes, COGS, debts, operating costs, depreciation, and interest payments.
For example, the same t-shirt company from before also pays for warehouse space, advertisements, and small business loan payments. So, the net profit would be how much is left over after all of that is covered. To find the net profit margin, you divide the net income by total revenue, creating a ratio. You can then multiply by 100 to make a percentage.
The formula for calculating net profit margins is:
Net Profit Margin = (Net Profit / Revenue) x 100
In this formula:
- Net profit is the same as net income: the amount left over after all costs are accounted for.
- Revenue is how much money was generated by the company by selling products, goods, or services.
- Multiply by 100 to create a percentage.
>>MORE: Explore the top companies in the finance field for 2025.
How to Calculate Operating Profit Margin
Operating profit (or operating income) is a company’s revenue after covering operating expenses, like COGS, employee wages, depreciation, and amortization. However, operating profits are pre-tax and pre-interest, meaning the revenue available before a company pays its income and property taxes and interest payments.
Think of operating profit as a step between gross profit and net profit — for gross profit, only COGS is subtracted from revenue, and for net profits, all expenses are subtracted, including taxes and interest. Operating profit is useful to know because you can easily compare it to other companies in other states that may have different tax rates. You can also use it to determine if a company is managing operating expenses effectively.
The formula for calculating operating profit margins is:
Operating Profit Margin = (Operating Profit / Revenue) x 100
In this formula:
- Operating profit is remaining revenue after subtracting operating expenses.
- Revenue is profits generated from the sale of goods, products, and services.
- Multiply by 100 to create a percentage.

Citi Finance
Explore how finance teams manage business KPIs (like profits), financial risks, and predict credit card sales with this free job simulation from Citi.
Avg. Time: 5 to 6 hours
Skills you’ll build: Fact finding, data analysis, communication, presentation, Basel III regulation, judgment, commercial awareness
Calculating Profit Margins: Examples
Let’s take a look at Apple. Using Apple’s 2023 annual report, we can figure out its profit margins for 2023.
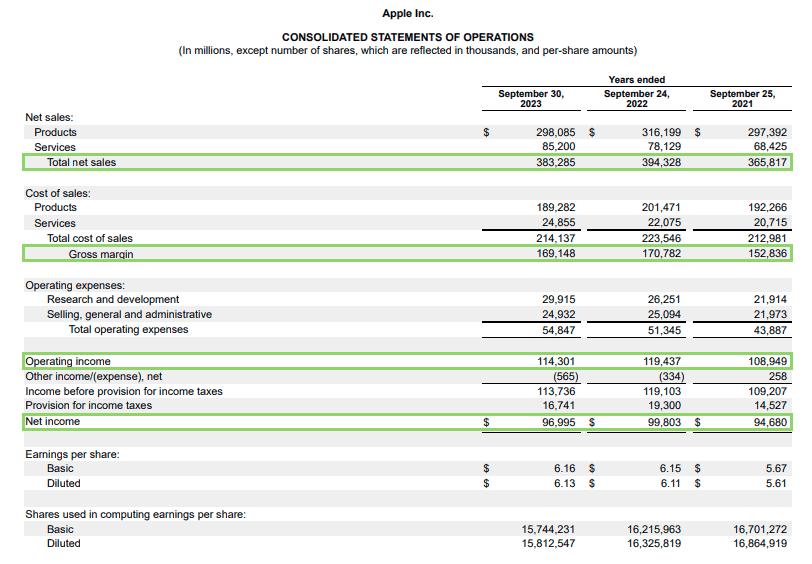
From Apple’s consolidated statement of operations, we can see the following details:
- Apple’s total net sales (revenue) for 2023: $383,285 million
- Apple’s gross margin (gross profit) for 2023: $169,148 million
- Apple’s net income (net profit) for 2023: $96,995 million
- Apple’s operating income (operating profit) for 2023: $114,301 million
To determine the gross profit margin, we need to divide the gross profit by the total revenue for the year and then multiply by 100.
( $169,148m / $383,285m ) x 100
- Apple’s gross profit margin for 2023 is: 44.1%
To determine the net profit margin, we need to divide the net income (or net profit) by the total revenue for the year and then multiply by 100.
( $96,995m / $383,285m ) x 100
- Apple’s net profit margin for 2023 is: 25.3%
To determine the operating profit margin, we need to divide the operating income or operating profit by the company’s total revenue and then multiply by 100.
( $114,301m / $383,285m ) x 100
- Apple’s operating profit margin for 2023 is: 29.8%
Find Your Career Fit
Unsure what job is right for you? Find out with our free career quiz!
How to Show Profit Margin Knowledge on Your Resume
Your resume should include any past coursework, work, or internship experiences that dealt with business valuation methods or tracking companies’ profitability, since these skills imply an understanding of profit margins.
You can also mention profit margins directly. For instance, in the description of a job or internship, you could say you “calculated profit margins for a company worth $X amount” or that you calculated and compared profit margins for companies across various industries.
Your cover letter is another great place to talk about your experience with profit margins. For example, you can mention if your relative has a small business and you helped them look at their profit margins to find areas where cutting costs would have a big impact.
>>MORE: Explore more accounting skills you need for your resume.
Related Finance Skills
Calculating profit margins is only one way to determine a company’s profitability. Accountants and finance professionals need to understand other ways to measure a business’s success, such as::
- Determining contribution margins for goods, products, and services
- Calculating compound annual growth rate (CAGR)
- Using business valuation approaches, such as discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis
- Performing comparable company analysis
- Measuring internal rates of return
Start learning these skills today with Forage’s free accounting job simulations.
FAQ
You can calculate profit margins backward to get an idea for how much to charge for a single product or to determine how much revenue you’ll need to make to offset your expenses.
Let’s say you want a 20% profit margin on sales for your t-shirt company and the t-shirts cost you $5 each to make. To figure out how much to charge per shirt, turn the 20% into a decimal point by dividing it by 100: 0.20. Then, subtract 0.20 from 1 to get 0.80 — this is the other 80% of revenue that will be offset by the cost of the product. So, divide your expenses for making the shirts (5.00) by 0.80 to determine how much to charge per shirt to guarantee a 20% profit margin.
5.00/0.80 = $6.25
What counts as a “good” profit margin depends largely on the company and industry. In general, a 5% profit margin is considered fairly low, meaning the product is expensive to produce and does not generate a lot of revenue.
A 10% profit margin is typically considered healthy or average — it’s high enough to ensure profits but not so high that the product is grossly overpriced.
A 20% margin is high, which can be good for many companies — more profits are typically good. However, high profits means the product is being sold for significantly more than it costs to produce, which may not be sustainable as, among other things, consumers may eventually try to find a cheaper option.
A product’s markup is the difference between its cost price and sales price. For example, if you buy keychains wholesale, and each keychain costs you $1, selling each for $5 would be a $4 markup.
A product’s profit margin can be equal to its markup. However, for more labor-intensive products, some profit margin formulas take into account peripheral expenses, like employee wages and transportation costs, which may not be reflected in a product’s markup.
Profit margins tell you how much a company makes from selling goods, products, and services, after accounting for all direct and indirect costs. It is a measure of profitability displayed as a percentage — a higher percentage means higher profits.
Image credit: IgorVetushko / Depositphotos.com

